Driving Rural Prosperity: The State of Rural America
Working-Age Populations Shrink While Older Populations Grow in Rural America:
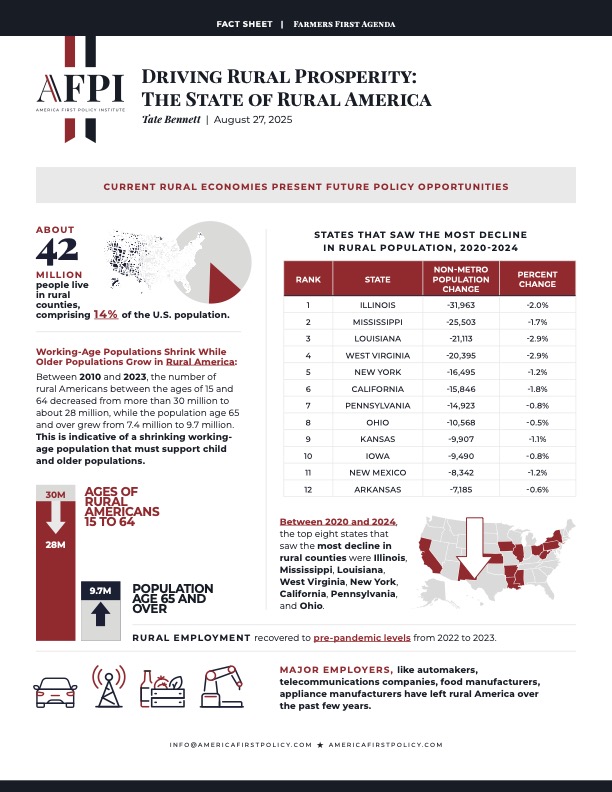
Between 2020 and 2024, the top eight states that saw the most decline in rural counties were Illinois, Mississippi, Louisiana, West Virginia, New York, California, Pennsylvania, and Ohio
Between 2010 and 2023, the number of rural Americans between the ages of 15 and 64 decreased from more than 30 million to about 28 million, while the population age 65 and over grew from 7.4 million to 9.7 million. This is indicative of a shrinking working-age population that must support child and older populations.
States That Saw the Most Decline in Rural Population, 2020-2024
Rank |
State |
Non-Metro Population Change |
Percent Change |
1 |
Illinois |
-31,963 |
-2.0% |
2 |
Mississippi |
-25,503 |
-1.7% |
3 |
Louisiana |
-21,113 |
-2.9% |
4 |
West Virginia |
-20,395 |
-2.9% |
5 |
New York |
-16,495 |
-1.2% |
6 |
California |
-15,846 |
-1.8% |
7 |
Pennsylvania |
-14,923 |
-0.8% |
8 |
Ohio |
-10,568 |
-0.5% |
9 |
Kansas |
-9,907 |
-1.1% |
10 |
Iowa |
-9,490 |
-0.8% |
11 |
New Mexico |
-8,342 |
-1.2% |
12 |
Arkansas |
-7,185 |
-0.6% |
About 42 million people live in rural counties, comprising 14% of the U.S. population.
Current Rural Economies Present Future Policy Opportunities
Rural employment recovered to pre-pandemic levels from 2022 to 2023. Major employers, like automakers, telecommunications companies, food manufacturers, and appliance manufacturers have left rural America over the past few years.
In 2021, students or nearly 10 million public school students attended rural schools in the fall 2022.
Rural Schools
Rural schools often face more challenges with respect to transportation costs, teacher recruitment and retention, and broadband. In 2021, 21% of rural residents aged 25 or higher had a bachelor’s degree or higher, compared to 35% in metro areas.
Hospital Closures
According to the GAO, 101 (4%) of rural hospitals closed between 2013-2020. When rural hospitals close, rural patients must travel longer distances for the same services— about 20 miles more for inpatient care, and 40 miles more for less common services like drug abuse treatment.
Veterans
In recent years, 1/3 of veterans enrolled in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) lived in rural America. They often face unique barriers to addressing mental health care such as staffing and transportation.
Maternal Care
More than half of rural counties lack hospital-based obstetric services. By 2030, the OB/GYN anticipated supply is expected to meet only about 50% of the demand in rural areas. Pregnancy-related and postpartum death rates are also higher in rural areas.